- Industries
- Automotive
3D Printing is revolutionising the transport industry with not only prototypes during the design and development stages, but with tooling, moulds, and even end-use parts during the manufacturing and production process.


- Jewelry
Produce high precision, functional 3D prints that can stand in for final parts and stand up to the rigors of the factory floor, from pre-production validation to jigs and fixtures to end-use parts


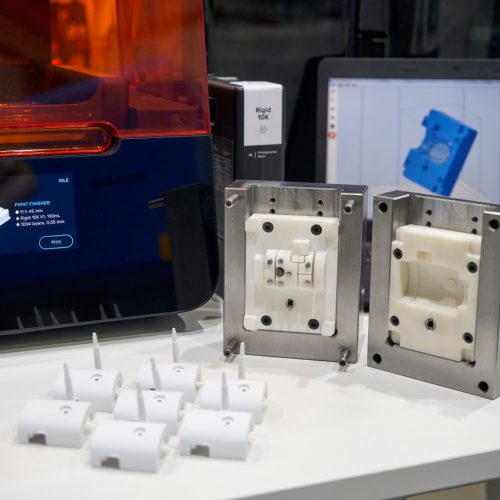
- Manufacturing
Manufacturing is experiencing a digital transformation with the advance of 3D printing in modern manufacturing facilities. The current strategic imperative is to embrace the breakthrough potential of 3D printing by integrating digital into your organization’s structures, processes, systems and incentives.


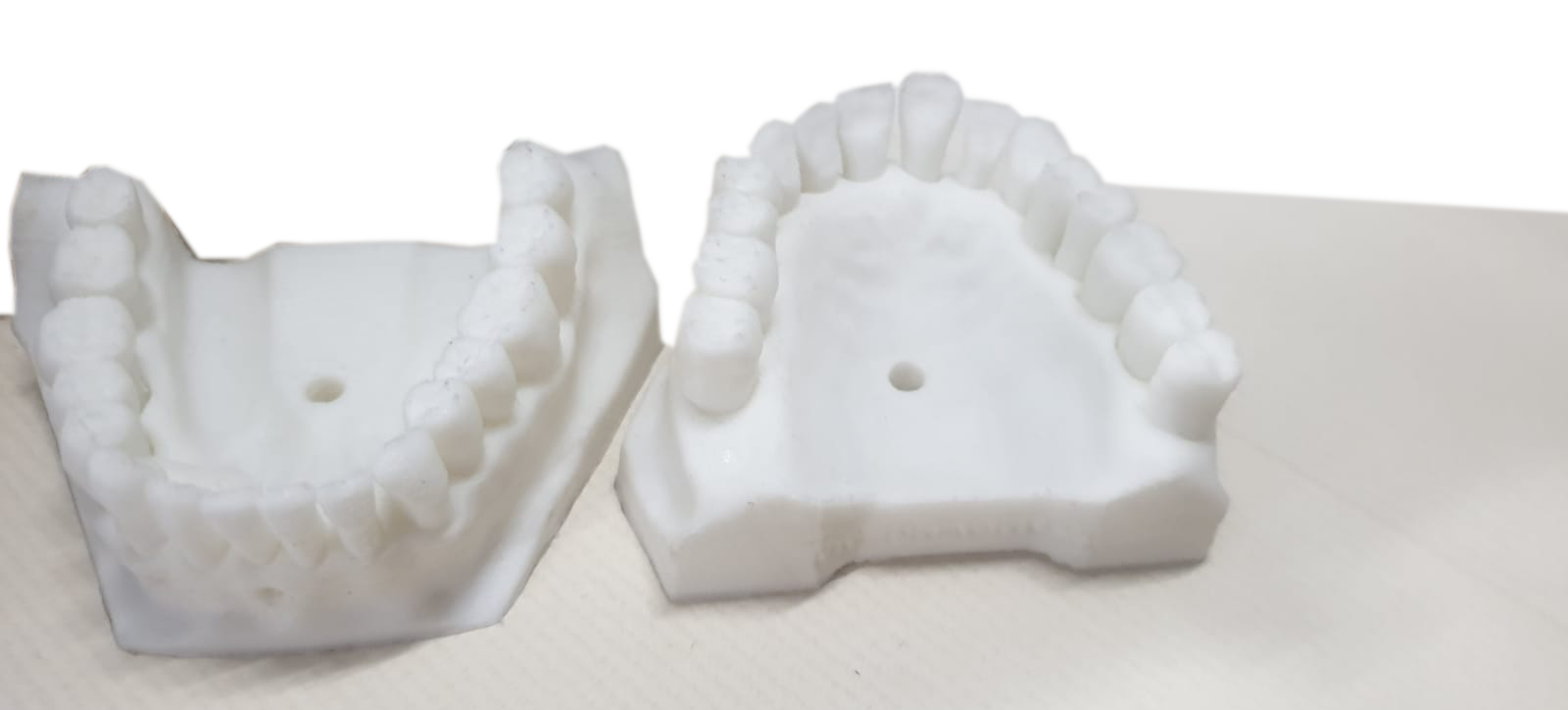
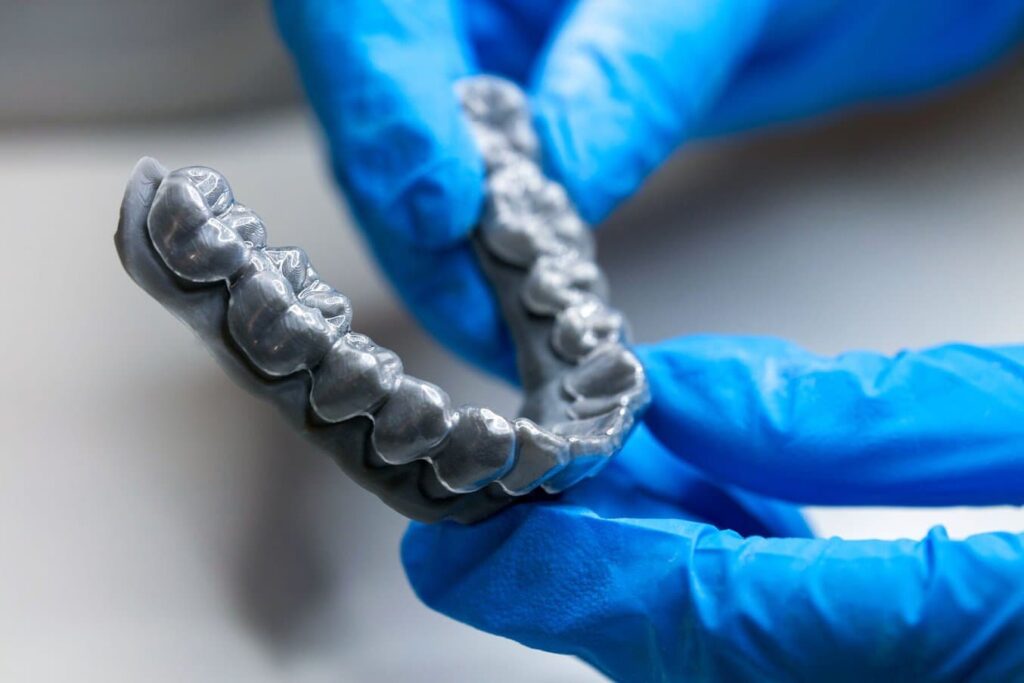
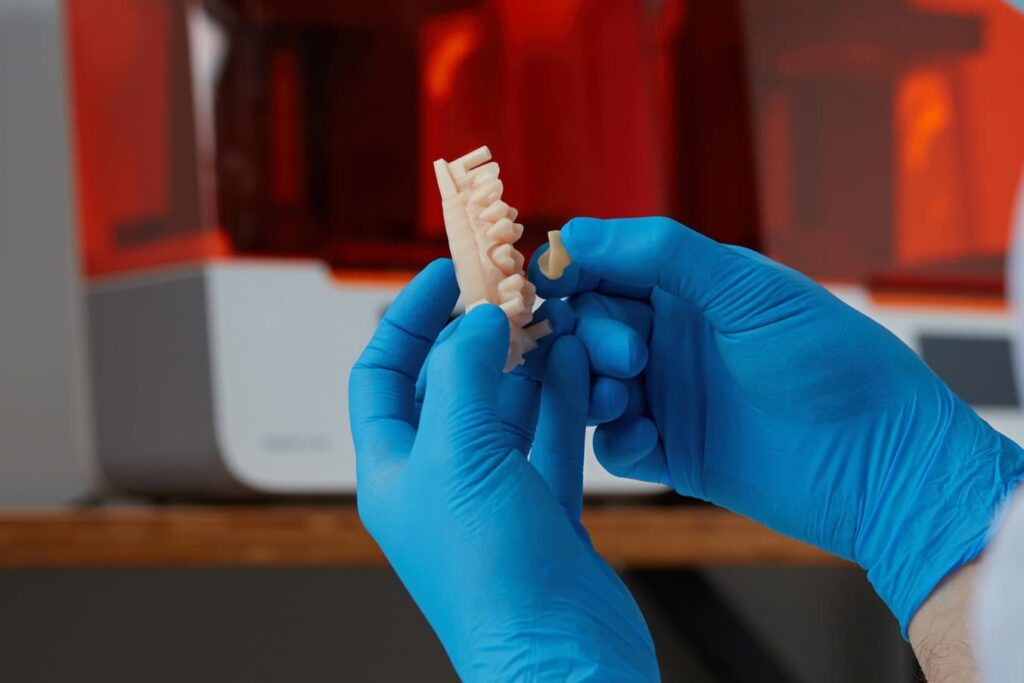
- Dental
Learn how dental labs and practices of any size can build reliable, high quality, easy-to-use digital workflows for dental models, surgical guides, splints, retainers, and more. 3D printing is revolutionizing the way surgeries are done.


- Entertainment
Use accessible, professional 3D printing to facilitate collaboration, win over directors, and bring hyper-realistic digital models to life in a matter of hours.


- Medical
Low Investment, High Impact. Open the door to high-impact medical applications, while saving significant time and costs from the lab to the operating room.


- Education
Bring the Real World to the ClassroomEncourage creativity and expose students to the same professional-level technology used by businesses in a range of industries.


- Engineering
Find Value Across the Supply Chain Produce high precision, functional 3D prints that can stand in for final parts and stand up to the rigors of the factory floor, from pre-production validation to jigs and fixtures to end-use parts


- Automotive
- 3D Printers
- 3D Printing Service
- About
- Support
- Blog