

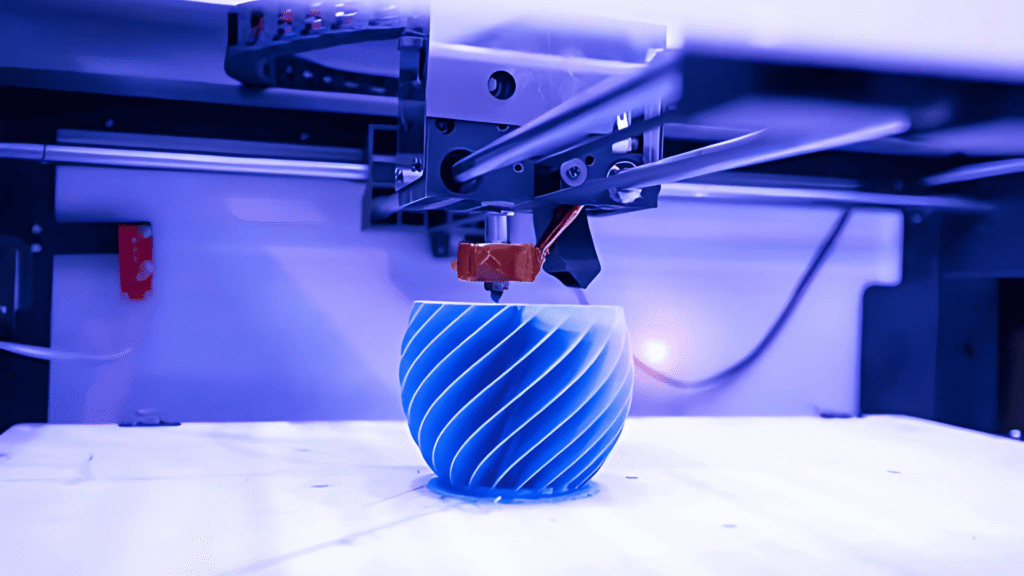
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) builds parts layer by layer using thermoplastic filament. It is cost-effective, widely adopted, and ideal for functional prototyping and low-volume production.
FDM technology transforms digital CAD files into durable physical models using a controlled heated nozzle and precision movement systems.
Ideal for geometric accuracy and repeatability, FDM enables cost-effective prototyping and production of custom parts.
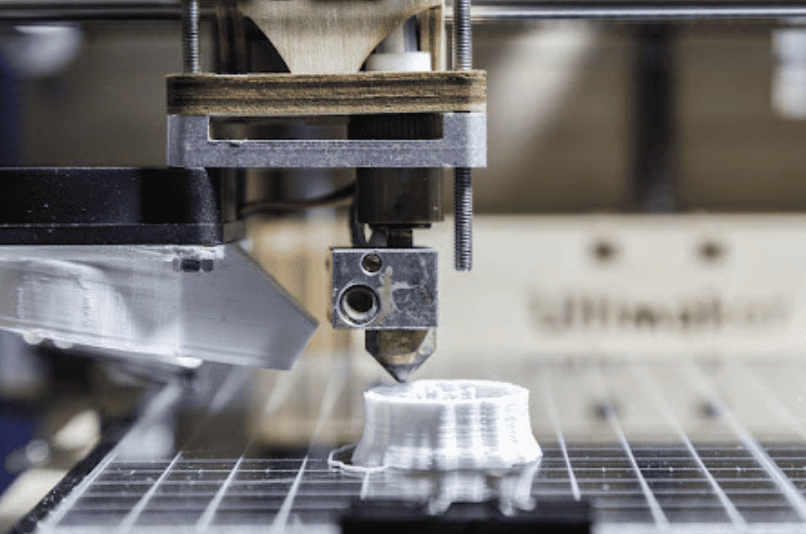
Quickly validate your product’s form, fit, and function using cost-effective FDM parts before committing to tooling or full-scale production.

FDM materials like ABS, Nylon, and PETG provide real-world mechanical performance for functional stress testing and validation.

Suitable for small-batch and on-demand production of durable components, enclosures, fixtures, or brackets ready for deployment.
Create custom jigs and fixtures quickly to improve assembly line precision, reduce setup times, and enhance operational safety.
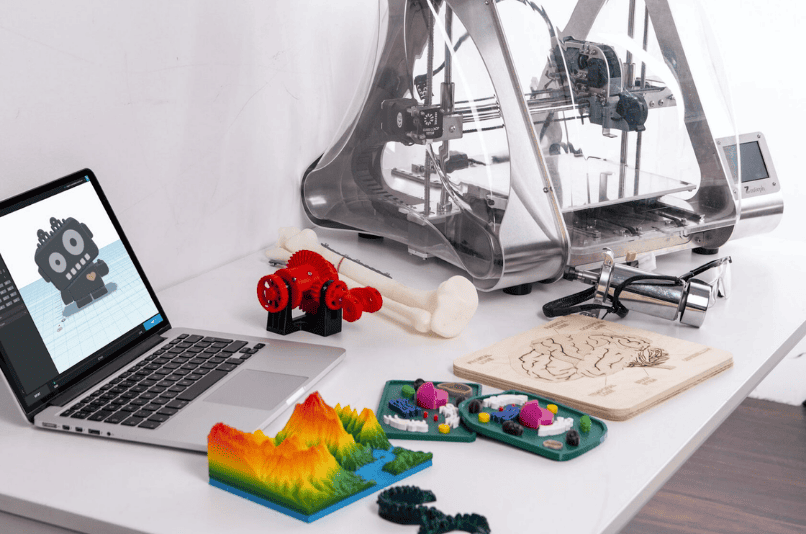

FDM is perfect for visual demonstrations, training aids, and academic environments where hands-on interaction is key.

Choose FDM when you need a budget-friendly solution for iterative design without compromising on basic strength and accuracy.
Cost-effective
FDM printers are among the most affordable 3D printers on the market, both in terms of machine price and material cost.
Wide material availability
Supports various thermoplastics like PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU, Nylon, etc., with many colors and properties.
User-friendly
Easy to set up, operate, and maintain. Ideal for hobbyists, students, and prototyping labs.
Good mechanical strength
Especially with materials like ABS and Nylon, FDM parts can be strong and durable.
Scalable
Available in multiple sizes, from desktop models to large industrial systems.
Minimal material waste
Material is deposited only where needed, reducing scrap.
Lower resolution and detail
Surface finish is rougher, with visible layer lines compared to SLA or SLS prints.
Warping and shrinkage
Common in materials like ABS due to uneven cooling, requiring heated beds or enclosures.
Supports required for overhangs
Complex geometries often need support structures, which add post-processing effort.
Limited material properties
While good for general use, FDM is not ideal for extremely high-performance or heat-resistant parts.
Post-processing needed
Sanding, polishing, or smoothing may be required for a professional finish.
Mechanical anisotropy
Strength varies by direction; parts are weaker between layers (Z-axis).
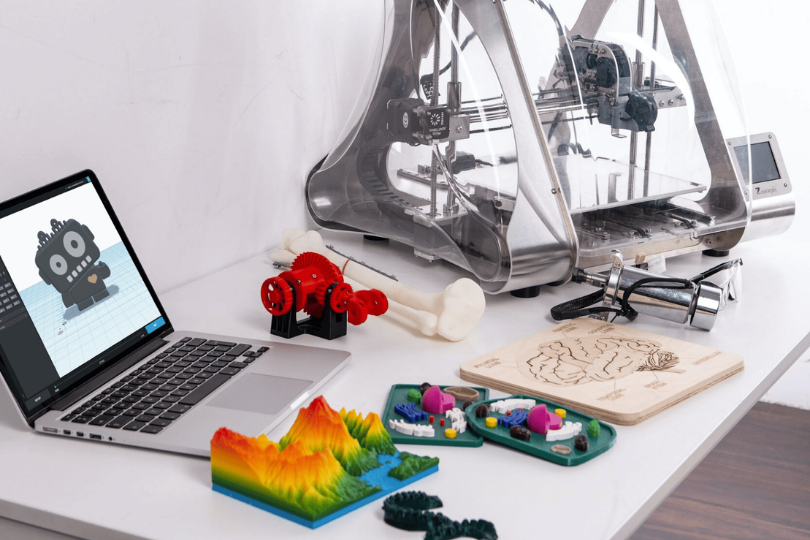

FDM 3D printing is transforming classrooms, labs, and design studios into innovation hubs. Students and educators use it for building mechanical models, architectural structures, STEM learning kits, and academic projects. It promotes hands-on learning and design thinking from school to university level.
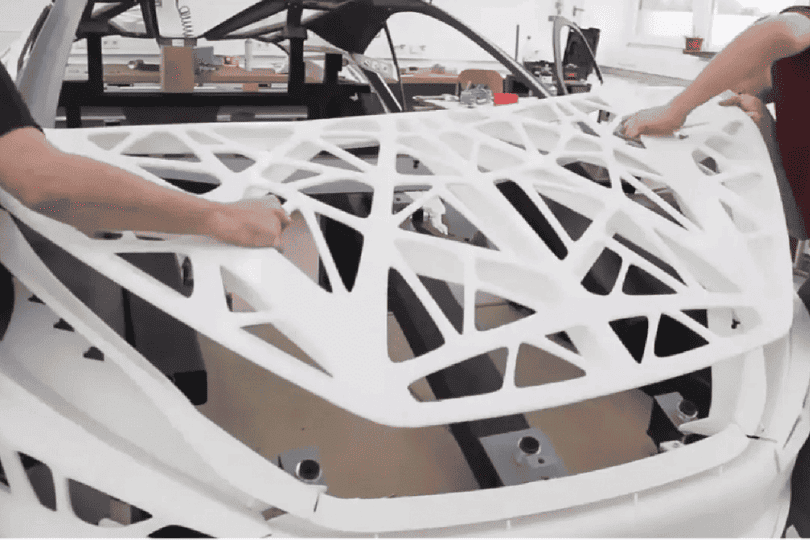

Automotive companies leverage FDM for producing custom jigs, fixtures, design validation models, airflow testing parts, and interior prototypes. It’s also used for testing ergonomic controls and developing short-run or discontinued replacement parts on demand.
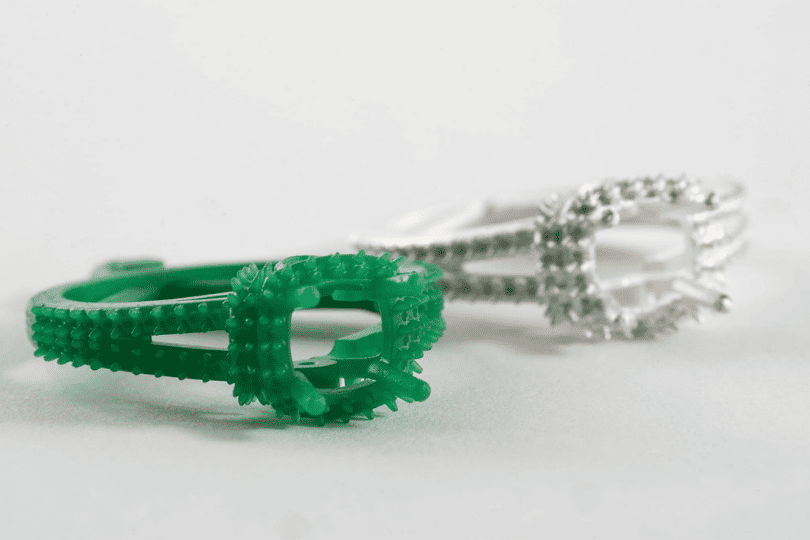
While traditionally served by resin printers, FDM is increasingly used in the design phase of jewelry development. Designers prototype ring bands, pendants, and settings to test form, scale, and fit before casting or final finishing in precious metals.
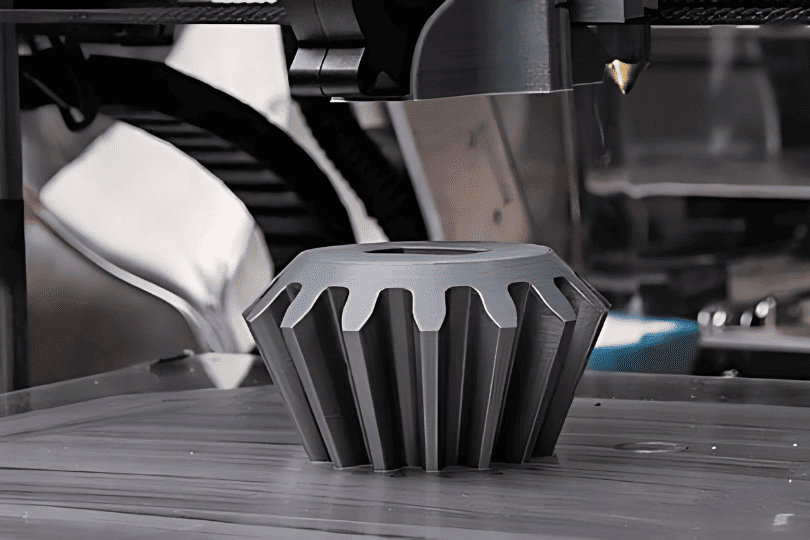
FDM empowers manufacturers to create low-cost tooling, alignment gauges, machine enclosures, and replacement parts. It enables lean, agile operations by reducing dependency on third-party tooling vendors and minimizing production delays.

FDM printing supports rapid development of surgical guides, custom casing for medical equipment, ergonomic grips for tools, and preoperative planning models. It’s commonly used for training aids and low-risk medical device development.
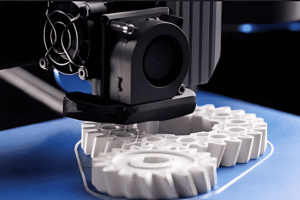
Engineers use FDM to develop, test, and refine complex parts quickly and cost-effectively. It facilitates rapid prototyping, stress testing, and assembling test rigs — bridging the gap between design and production.


















