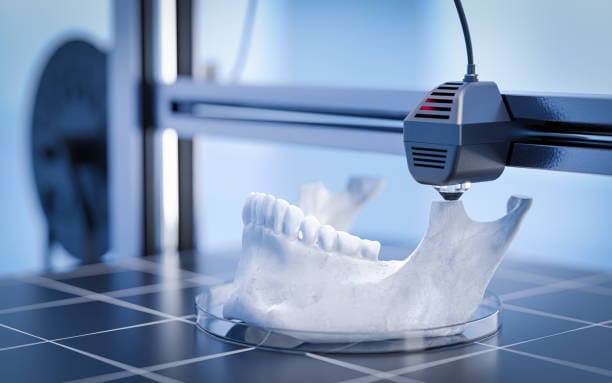
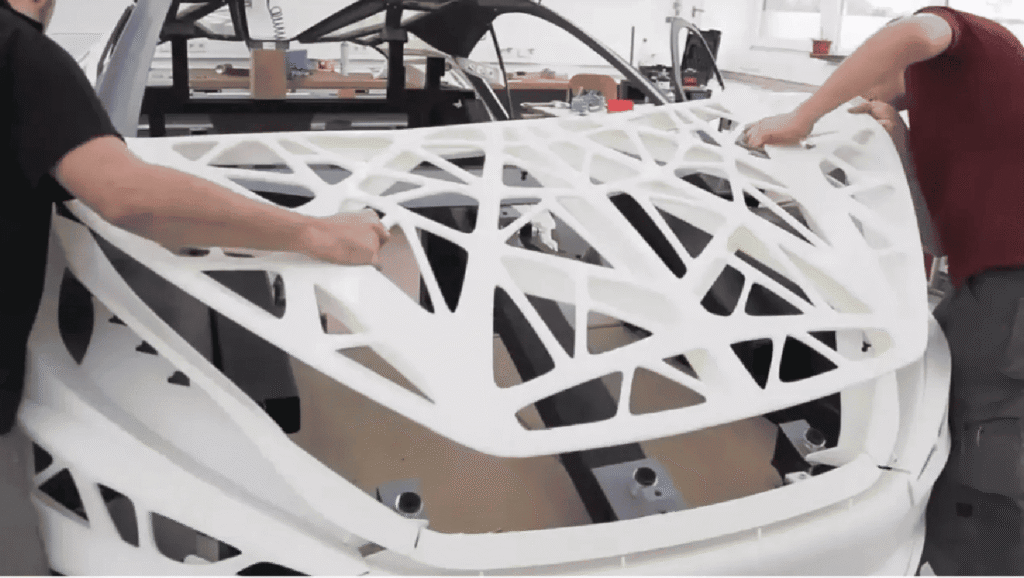
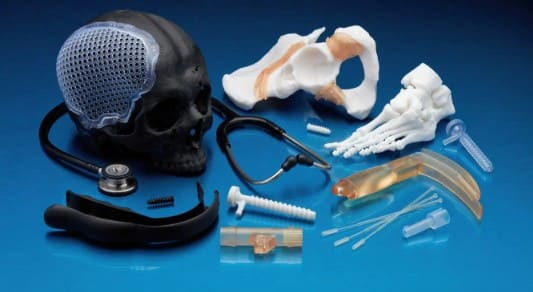
It combines toughness with clarity, making it ideal for parts that require strength, dimensional stability, and some transparency.
PC is commonly used in functional prototypes and end-use products that need to withstand stress and elevated temperatures.
PC combines exceptional durability, thermal and chemical resistance, and design flexibility, making it ideal for a wide range of demanding applications.
Polycarbonate stands as the temperature champion of 3D printing materials, maintaining its properties at temperatures that would destroy other thermoplastics. This engineering polymer combines extreme strength with heat resistance, making it indispensable for demanding thermal applications.
Exceptional Properties:
High-Performance Results: With an overall score of 3.5/5, PC’s rating reflects its specialized nature. For applications requiring transparency, heat resistance, or extreme toughness, PC is often the only viable option. The technical challenges are manageable with proper equipment.
Safety Notice: Polycarbonate releases potentially harmful fumes when printed. Always use in well-ventilated areas or with proper fume extraction. Not recommended for home use without appropriate safety measures.